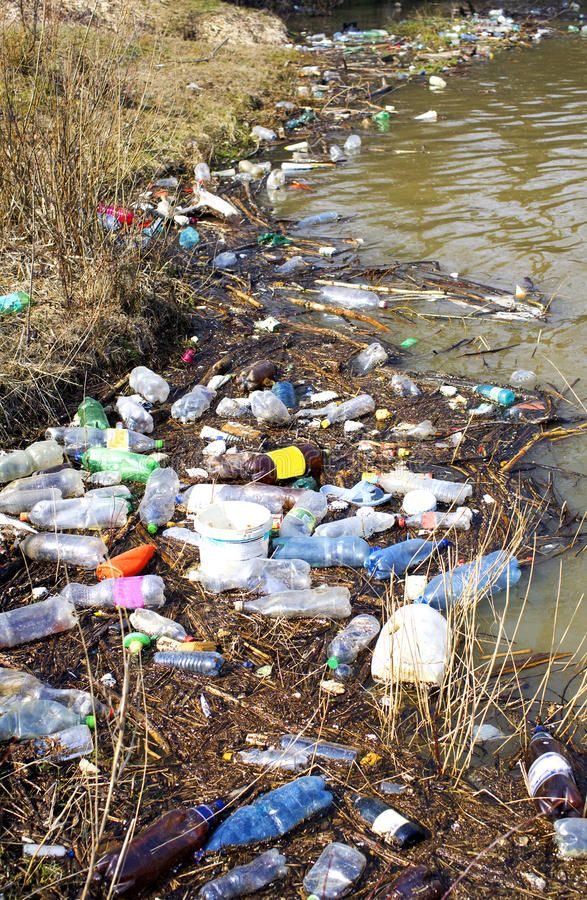
Overview of Plastic Usage in Uganda
Uganda, like many countries worldwide, faces significant challenges due to the widespread use of plastics. The convenience of plastic materials has led to their pervasive presence in daily life, from packaging and containers to single-use bags and bottles. However, this convenience comes at a substantial environmental cost.
Effects of Plastic Pollution
Environmental Impact: Plastic waste significantly affects Uganda’s natural landscapes, waterways, and wildlife. Non-biodegradable plastics accumulate in the environment, leading to soil and water pollution. This pollution is particularly evident in urban areas like Kampala, where drainage systems are often clogged with plastic bags, causing floods during the rainy seasons.
Health Implications: The improper disposal of plastic waste can lead to the breeding of disease vectors such as mosquitoes. Additionally, when plastics are burned as a method of disposal, harmful chemicals are released into the air, contributing to respiratory issues among the local population.
Economic Consequences: The tourism industry, which contributes significantly to Uganda’s economy, could suffer due to the unsightly nature of plastic litter. Pristine natural environments are crucial for attracting tourists, and plastic pollution undermines this asset.

Statistics on Plastic Usage in Uganda
While specific data can vary, recent studies indicate that Uganda generates substantial plastic waste, particularly in urban centers. For instance, Kampala alone is estimated to produce over 1,400 tons of solid waste daily, a significant portion of which is plastic. Moreover, less than half of this waste is properly collected and disposed of, exacerbating the pollution problem.
Legislative Measures and Their Effectiveness
In response to the growing crisis, the Ugandan government has taken legislative steps, such as the ban on lightweight plastic bags. However, enforcement remains a challenge. The proliferation of illegal production and importation of banned plastics continues to undermine these regulatory efforts.
Solutions and Recommendations
Strengthening Legislation and Enforcement: To combat the influx of illegal plastics, there needs to be stricter enforcement of existing laws and penalties for violations. Additionally, the government should consider expanding the scope of the ban to include other types of single-use plastics.
Promoting Alternative Materials: Encouraging the use of biodegradable or reusable alternatives can significantly reduce plastic waste. Initiatives to support local production of these alternatives can also foster economic opportunities.
Enhancing Waste Management Systems: Improving waste collection, sorting, and recycling facilities is crucial. Public-private partnerships could be instrumental in establishing more efficient and widespread waste management infrastructure.
Public Education and Awareness: Continuous public education campaigns are necessary to change consumer behavior and promote responsible plastic usage and disposal. Schools, media, and community leaders can play pivotal roles in these educational efforts.
Community Cleanup Initiatives: Organizing regular community cleanup activities can help manage the existing waste and foster community spirit and responsibility towards maintaining a clean environment.
Conclusion
The challenge of plastic pollution in Uganda requires a multi-faceted approach involving government action, community involvement, and individual responsibility. By implementing robust policies, promoting sustainable alternatives, and enhancing public awareness, Uganda can address the pressing issue of plastic pollution and pave the way for a cleaner, healthier environment.