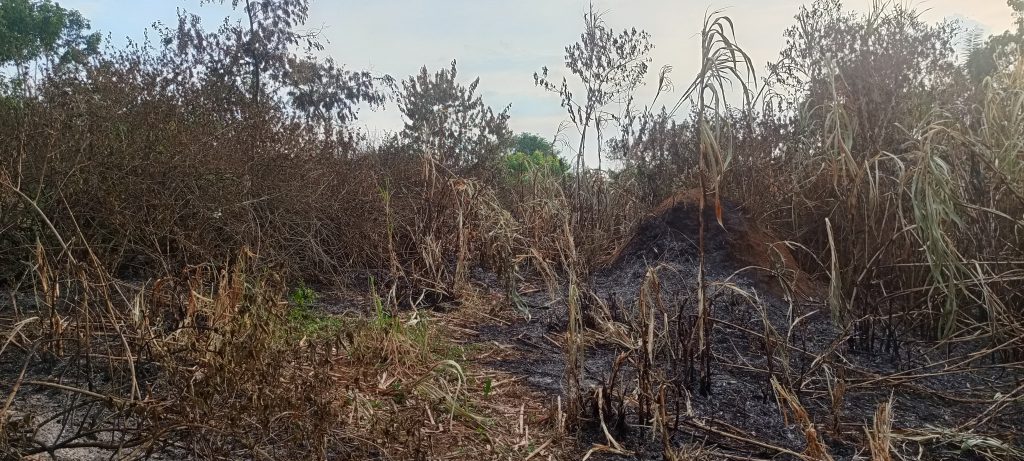
Deforestation stands as one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time, affecting ecosystems, biodiversity, and climate stability worldwide. In this blog post, we delve into the causes behind deforestation, its far-reaching impacts on the environment, and explore potential solutions to mitigate this critical challenge.
Causes of Deforestation
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses or due to natural causes, has several underlying causes, including:
Agriculture: Conversion of forest land for agricultural purposes, including large-scale farming and small-scale subsistence agriculture.
Logging: Timber harvesting for wood products and fuel is a significant cause, both legally and illegally.
Infrastructure Expansion: Building roads, highways, and urban areas often necessitates clearing forests.
Mining: Extraction of minerals and natural resources requires large areas of land to be cleared, impacting forests.
Climate Change: Changes in climate patterns can contribute to deforestation through droughts and wildfires.
Population Growth: Increasing human populations can lead to higher demand for resources, driving deforestation.
Fire: Forest fires, whether natural or human-caused, can devastate large areas of forest.
Illegal Activities: Illegal logging, hunting, and land grabbing can contribute significantly to deforestation.
Infrastructure Development: Hydroelectric dams and reservoirs can flood large areas of forested land.
Commercial Agriculture: Expansion of plantations for crops such as palm oil, soybeans, and cattle ranching.
Impacts on the Environment
Loss of Biodiversity: Forests harbor a vast array of plant and animal species. Deforestation disrupts ecosystems, leading to species extinction and loss of biodiversity.
Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation releases stored carbon and reduces the planet’s capacity to mitigate climate change.
Soil Erosion and Degradation: Tree roots help bind soil together. Without them, deforested areas are prone to erosion, leading to loss of fertile soil and increased sedimentation in rivers and lakes.
Disruption of Water Cycles: Forests play a crucial role in regulating water cycles. Deforestation can disrupt rainfall patterns, leading to altered water availability and increased risks of droughts and floods.
Solutions to Deforestation
Sustainable Land Use Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture and forestry practices that prioritize conservation and regeneration of forests.
Protecting Forests: Establishing and enforcing protected areas and national parks to conserve biodiversity and prevent further deforestation.
Reducing Consumption of Unsustainable Products: Supporting sustainable supply chains and consumer choices that avoid products linked to deforestation, such as palm oil and tropical hardwoods.
Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees and restoring degraded lands to enhance carbon sequestration, restore habitats, and improve ecosystem services.
Policy Interventions: Implementing policies and incentives that promote forest conservation, enforce sustainable land use practices, and penalize illegal logging and land clearance.